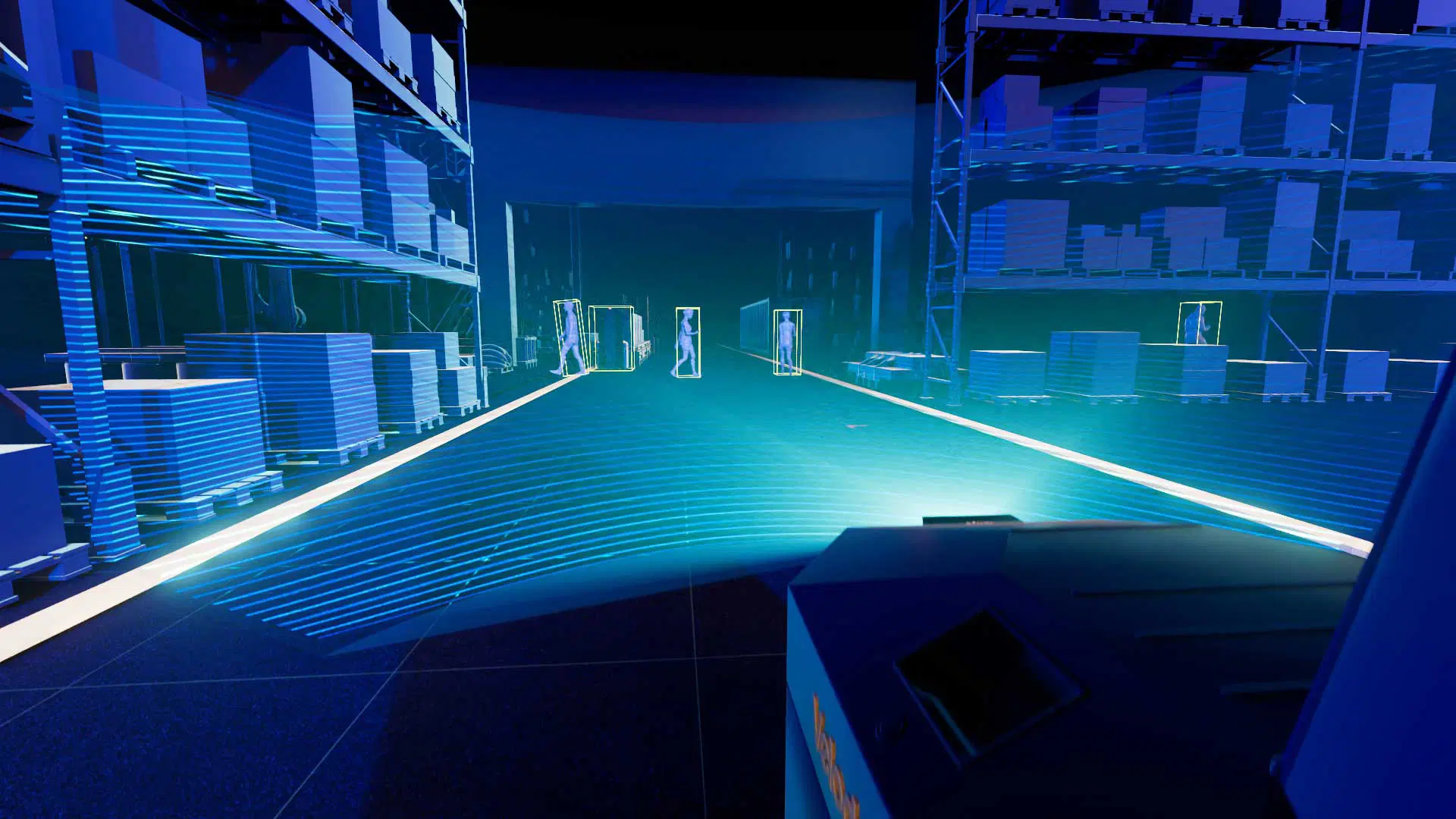
How does Lidar work?
1.
A typical lidar sensor emits pulsed light waves into the surrounding environment.

2.
These pulses bounce off surrounding objects and return to the sensor.
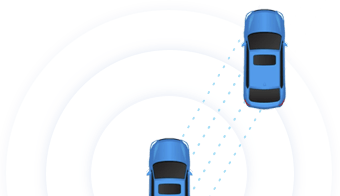
3.
The sensor uses the time it took for each pulse to return to the sensor to calculate the distance it traveled.
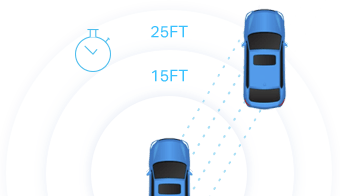
Repeating this process millions of times per second creates a precise, real-time 3D map of the environment. This 3D map is called a point cloud. An onboard computer can utilize the lidar point cloud for safe navigation.

